Botox is a neuromodulator with a range of applications in modern medicine. While widely recognized for its use in cosmetic procedures to smooth facial lines, its therapeutic uses extend to a variety of medical conditions. The substance’s mechanism of action, which involves modulating nerve signals, allows qualified clinicians to use it for both aesthetic and therapeutic purposes.
What Is Botox?
Botox is a brand name for a specific type of botulinum toxin. In medical settings, practitioners use a highly purified form of this substance. When administered in controlled doses, it works by temporarily interrupting signals from nerves to specific muscles. This targeted action prevents the muscle from contracting without affecting other parts of the body. This precise modulation of nerve signals is the basis for its use in treating a wide array of medical conditions.
What Is It Used For?
The therapeutic applications of botulinum toxin are diverse and address conditions affecting various body systems. It is used as part of established treatment protocols for chronic migraines, helping to reduce the frequency of headache days. In neurology, it is applied to manage muscle disorders like cervical dystonia, a condition causing involuntary neck muscle contractions. It is also used to manage spasticity associated with conditions like cerebral palsy.
Another application is in the management of hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. Urologists may use botulinum toxin to treat overactive bladder and urge incontinence in patients who do not respond to other medications. Ophthalmologists also use it to treat eye conditions, including crossed eyes, by relaxing eye muscles.
What Does the Process Involve?
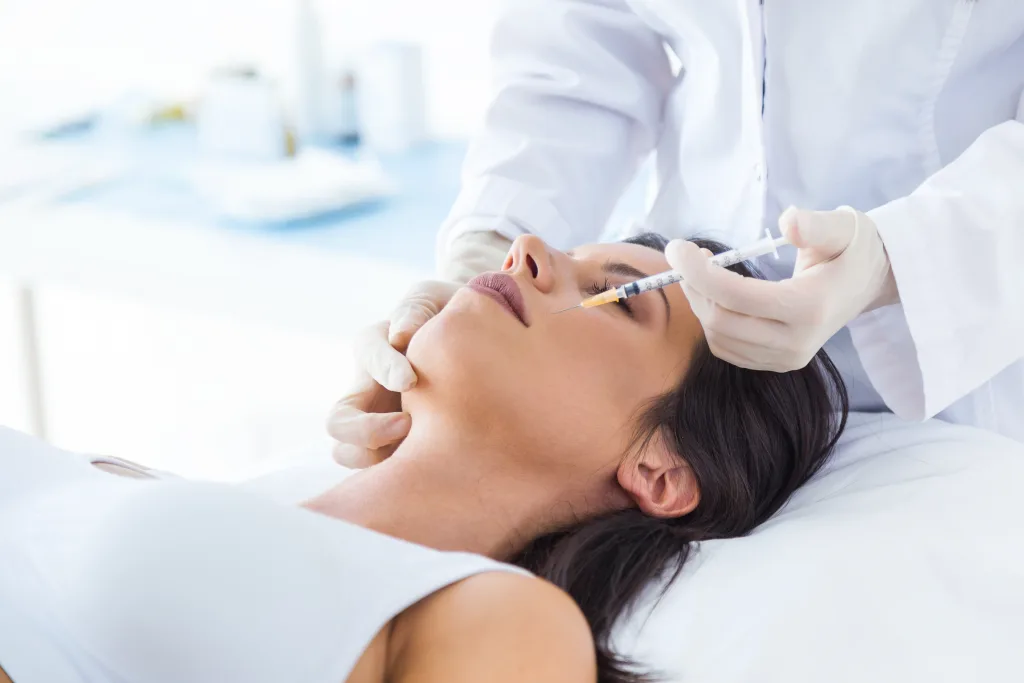
The administration of botulinum toxin begins with a thorough consultation with a qualified provider. During this meeting, the clinician assesses the patient’s medical history, discusses symptoms, and determines if this treatment is an appropriate option. The dosage used varies significantly depending on the indication. Larger muscle groups or more severe conditions may require different doses than smaller areas.
This procedure can be performed in an office setting and is relatively brief. The clinician injects the substance into the targeted muscles or glands using a fine needle. Patients generally report minimal discomfort during the process. After the injections, individuals can usually resume their normal activities with few restrictions.
The time it takes to notice changes can range from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the individual and the condition. The effects are temporary, and their duration may last for several months before gradually tapering off. As the effects wear off, muscle or gland activity will return to its previous state. Common side effects discussed with patients are typically localized and may include soreness, swelling, or bruising at the injection sites.
Seek Professional Dermatology Services
Understanding the range of botulinum toxin’s applications is the first step, but seeking personalized medical guidance is the next. A consultation with a licensed and experienced provider, such as a dermatologist, is necessary to determine if this treatment is suitable for your specific needs. A dermatologist can perform a comprehensive evaluation of your condition, discuss potential risks and benefits, and coordinate care with other specialists if needed.