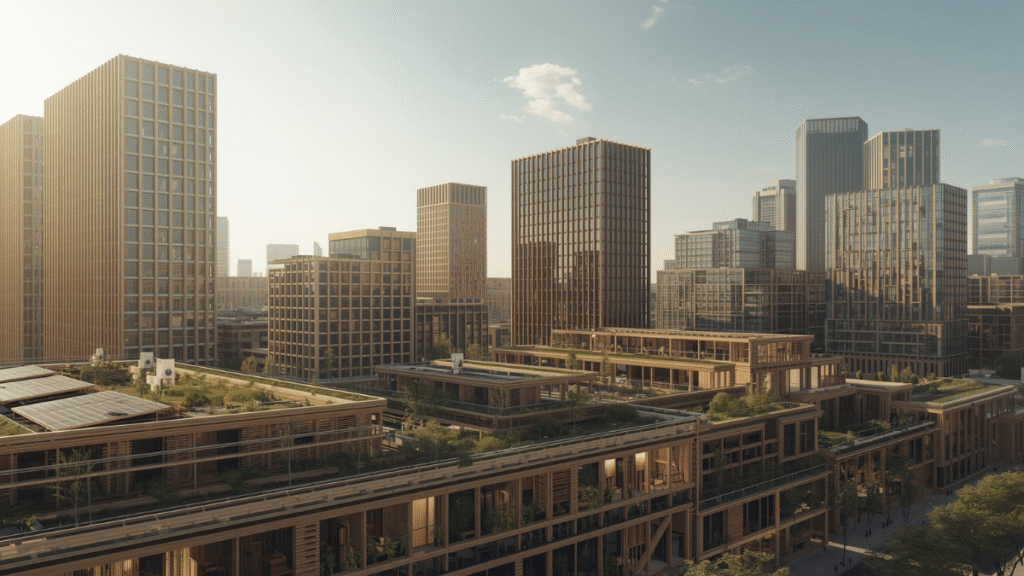
Discover the benefits, history, and innovations of mass timber architecture. Learn how it promotes sustainability, efficiency, and beauty in modern construction.
also read: https://upnaboves.com/upnabove-com-about-page/
Introduction to Mass Timber Architecture
Mass timber architecture is transforming the way we think about building design. Unlike conventional concrete and steel construction, this innovative method uses large, engineered wood panels to create strong, sustainable, and visually appealing structures. With growing concerns about climate change, carbon emissions, and eco-friendly building solutions, mass timber has gained global recognition as one of the most promising alternatives in modern architecture.
From high-rise buildings to community centers, schools, and offices, mass timber architecture combines sustainability with cutting-edge design, proving that eco-conscious choices can also be stylish and durable.
What is Mass Timber Architecture?
Mass timber refers to structural wood products that are manufactured by bonding multiple layers of lumber together. This process creates large panels and beams with incredible strength, making them suitable for constructing multi-story buildings. Unlike traditional timber framing, mass timber uses advanced engineering to enhance fire resistance, load capacity, and durability.
Some of the most common types of mass timber products include:
| Mass Timber Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) | Layers of wood glued at 90° angles | Floors, walls, roofs |
| Glue-Laminated Timber (Glulam) | Multiple wood laminations bonded together | Beams, columns |
| Nail-Laminated Timber (NLT) | Boards stacked and nailed together | Floors, decking |
| Dowel-Laminated Timber (DLT) | Boards joined with wooden dowels | Flooring, panels |
These engineered wood systems allow architects to design structures that are lightweight yet remarkably strong.
The Rise and History of Mass Timber
The roots of mass timber architecture can be traced back to Europe, particularly Austria and Germany, where CLT was first developed in the 1990s. Since then, the technology has rapidly spread across North America and Asia, gaining traction in both residential and commercial sectors.
Historically, wood has always been one of the oldest building materials. However, with the industrial age came steel and concrete, which dominated modern construction. Today, as environmental concerns grow, the industry is shifting back to wood—but this time, through advanced mass timber technology that addresses strength, durability, and fire safety.
Benefits of Mass Timber Architecture
1. Sustainability and Carbon Reduction
Mass timber significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to concrete and steel. Trees naturally absorb carbon dioxide, and when used in buildings, this carbon is stored for decades. This makes mass timber architecture a powerful tool in the fight against climate change.
2. Speed of Construction
Mass timber panels are prefabricated off-site and then assembled on-site. This reduces construction time, labor costs, and disruptions in urban environments.
3. Aesthetic Appeal
The natural beauty of wood creates warm, inviting interiors that promote well-being. Exposed timber elements are increasingly popular in offices, homes, and community spaces.
4. Fire Resistance
Contrary to misconceptions, mass timber performs well in fire tests. When exposed to fire, the outer layer chars, which insulates and protects the inner structure.
5. Lightweight but Strong
Mass timber structures are lighter than concrete, reducing foundation requirements while still providing exceptional strength and stability.
Applications of Mass Timber in Modern Architecture
Mass timber is no longer limited to small residential projects. Today, architects and developers are exploring bold new applications.
- High-Rise Buildings – Several skyscrapers around the world are being constructed with mass timber, challenging the dominance of steel and concrete.
- Educational Institutions – Schools and universities use timber to create sustainable, student-friendly learning environments.
- Community Centers and Libraries – Public spaces benefit from timber’s natural warmth and acoustic properties.
- Offices and Workspaces – Companies are choosing timber for healthier indoor air quality and biophilic design appeal.
Mass Timber vs. Concrete and Steel
To understand the value of mass timber architecture, let’s compare it to traditional building materials:
| Feature | Mass Timber | Concrete | Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint | Low | High | High |
| Construction Speed | Fast (prefabricated) | Slower | Medium |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Natural & warm | Industrial | Modern but cold |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent (char layer protection) | Good | Excellent |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy | Medium |
This comparison highlights why mass timber is becoming a preferred choice for sustainable cities.
Challenges Facing Mass Timber Architecture
Despite its many advantages, mass timber still faces certain challenges:
- Regulatory Barriers – Building codes in some countries limit timber use in high-rise construction.
- Supply Chain Limitations – Large-scale timber production requires sustainable forestry management.
- Cost Perception – Although costs are decreasing, mass timber is sometimes seen as more expensive upfront compared to conventional materials.
Addressing these challenges will be key to ensuring wider adoption in the future.
Innovations and Future of Mass Timber
The future looks promising for mass timber architecture. With new technologies, we are witnessing:
- Hybrid Buildings – Combining timber with concrete or steel for extra strength.
- Tall Timber Towers – Cities like Vancouver, Tokyo, and Vienna are setting global records for the tallest timber skyscrapers.
- Smart Prefabrication – Digital design tools and CNC machining allow precision manufacturing.
- Circular Economy Models – Timber elements can be reused or recycled, minimizing waste.
As governments push for net-zero carbon goals, mass timber will play an increasingly vital role in sustainable construction.
FAQs on Mass Timber Architecture
Q1: Is mass timber more expensive than concrete?
Mass timber may have slightly higher upfront costs, but its faster construction time and reduced labor often balance expenses.
Q2: How tall can mass timber buildings be?
With modern engineering, mass timber skyscrapers can reach 18–30 stories, and ongoing research is pushing these limits even higher.
Q3: Does mass timber require special maintenance?
Regular building maintenance is sufficient. Timber panels are treated for durability, moisture resistance, and long-term stability.
Q4: Is it safe to use mass timber in earthquake-prone areas?
Yes. Mass timber structures are lightweight and flexible, which gives them excellent seismic performance.
Q5: How long does mass timber last?
With proper design and maintenance, mass timber buildings can last as long as those made from steel or concrete.
Q6: Is mass timber environmentally friendly?
Yes. It uses renewable wood resources, reduces carbon emissions, and promotes sustainable forestry practices.
Q7: Can mass timber be used in combination with other materials?
Absolutely. Many hybrid projects combine timber with concrete or steel for optimal results.
Q8: Does mass timber reduce noise in buildings?
Yes. The solid wood panels have strong acoustic properties, reducing noise transfer between floors and rooms.
Q9: Where is mass timber most popular?
Countries like Canada, Austria, Germany, the U.S., and Japan are leading in mass timber adoption.
Q10: Can old mass timber be recycled?
Yes. Mass timber panels can be repurposed, recycled, or even used as biomass energy.
Conclusion
Mass timber architecture is not just a trend—it is the future of sustainable design. By offering durability, fire resistance, beauty, and eco-friendliness, it stands as a revolutionary alternative to concrete and steel. As global cities aim for greener, carbon-neutral solutions, mass timber will continue to shape the skylines of tomorrow.
With innovations in prefabrication, hybrid construction, and sustainable forestry, mass timber architecture provides a blueprint for how humanity can build responsibly while still embracing creativity and progress.
also read: https://upnaboves.com/upnabove-com/
also read:https://upnaboves.com/upnabove-com-innovations/
also read: https://upnaboves.com/upnabove-com-solutions/
also read: https://upnaboves.com/upnabove-com-uav/
also read: https://upnaboves.com/client-success-stories-transforming-spaces-with-upnaboves-com/
also read: https://upnaboves.com/how-upnaboves-com-helps-reduce-carbon-footprints-in-construction/