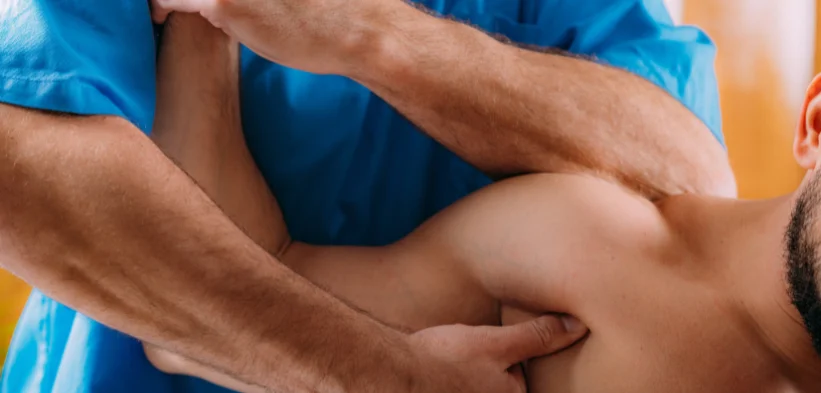
Arm pain presents as discomfort anywhere from the shoulder to the wrist, and its causes are numerous. While the experience of arm pain varies in intensity and character, seeking a structured treatment plan is a common step for those affected. Physical therapy offers a methodical approach to managing these symptoms, and it also addresses their underlying causes. Here is more information about the role of physical therapy:
Providing Pain Relief
Physical therapists use specific techniques to help lessen discomfort in the arm. Manual therapy, which includes techniques such as soft tissue massage and joint mobilization, may be applied to alleviate pain. Therapists also guide patients through targeted exercises and may use modalities such as heat or cryotherapy to manage symptoms.
Improving Flexibility
A primary goal of physical therapy is to restore and improve movement in the affected arm. Stretching exercises are used to lengthen tight muscles, while nerve glide techniques are used to improve the mobility of nerves that may be compressed or irritated. Improved flexibility may allow for easier completion of daily activities, although progress depends on consistent participation in the prescribed program.
When joint stiffness is a contributing factor, a physical therapist might use joint mobilization techniques to improve the joint’s range of motion. These are gentle, passive movements that the therapist applies to the affected joint. This approach aims to restore normal joint mechanics and function over time, and it is combined with active exercises performed by the patient.
For individuals experiencing persistent stiffness, a therapist may develop a more intensive program. This program could involve dynamic stretching, which is an advanced technique that targets both muscular and neural components of movement. The objective remains to increase the arm’s functional range of motion, so daily tasks become less challenging.
Reducing Inflammation
Physical therapy interventions also address inflammation, which is often a source of arm pain and limited function. Modalities such as cryotherapy, or cold application, may help constrict blood vessels to reduce swelling in acute injuries. Electrical stimulation techniques may also be used to assist with muscle function and fluid reduction around an inflamed area.
Leading to Other Approaches
When physical therapy does not fully resolve the symptoms, it provides valuable diagnostic information that guides subsequent medical steps. A patient’s response to specific movements and treatments helps a physician determine if other interventions are appropriate. This data may indicate the need for procedures such as nerve blocks. This is when medication is injected to interrupt pain signals.
In cases of chronic pain originating from specific joints, detailed feedback from a physical therapy course may suggest that a patient is a candidate for radiofrequency ablation. This procedure uses heat to target specific nerves and disrupt their ability to send pain signals. Some complex pain syndromes may not respond to initial treatments. Sometimes, therapy observations suggest the need for a spinal cord stimulation evaluation.
Get Treated for Arm Pain
Arm pain can interfere with work, hobbies, and simple daily tasks, but a structured treatment plan can help manage the condition. Physical therapy provides a foundation for addressing the mechanical and functional issues contributing to your discomfort. If you are experiencing persistent arm pain, schedule a consultation with a spine and pain specialist to discuss your symptoms and determine an appropriate treatment plan.