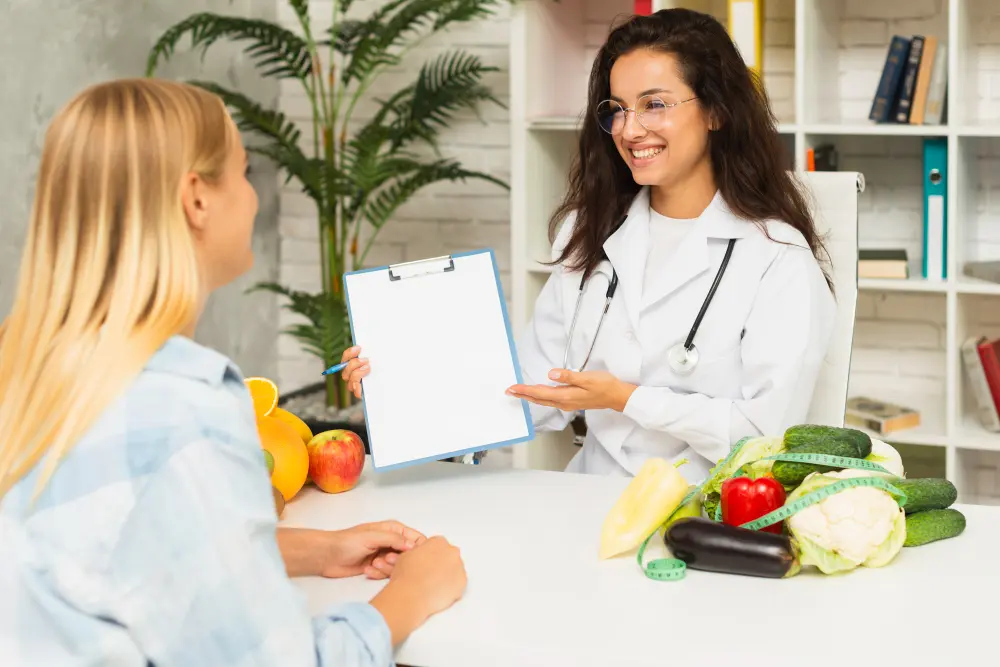
Depression is a complex mood disorder that affects how you feel, think, and handle daily activities. While professional treatment is the foundation of care, exploring supportive strategies, such as dietary adjustments, may offer additional avenues for managing symptoms. Understanding the connection between what you eat and how you feel is a practical step in a comprehensive wellness plan. Here is more information about the role of nutrition for depression:
Reducing Burden
Adjusting nutritional habits may influence the body’s inflammatory processes, which may be linked to depression. A diet that includes a variety of whole foods provides a range of nutrients, and this balanced intake can have a positive impact on overall well-being. It is helpful to eat healthy foods rich in nutrients rather than processed foods that lack many essential nutrients.
People make nutritional choices every day. Because diet is a modifiable lifestyle factor, individuals can make changes to their diet. These adjustments may complement other therapeutic approaches, making them helpful in your journey.
Providing Vitamins
Specific vitamins play a key role in the body’s neurological functions. B vitamins, for instance, play a role in producing brain chemicals that influence mood and other brain functions. Since the body does not store some B vitamins for long, maintaining their levels requires consistent dietary intake of foods rich in B vitamins, such as leafy greens, legumes, and eggs.
Vitamin D is another nutrient that has been studied for its role in mental health. The body produces vitamin D through sun exposure, but it is also found in certain foods, such as fatty fish and fortified milk. Many people have low levels of vitamin D, especially during winter months or in regions with limited sunlight. A healthcare provider can test for deficiencies and recommend appropriate steps if they find that your levels are low.
Adding Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat that the body cannot make on its own. These fats are a part of cell membranes throughout the body, including in the brain. They are found in sources such as:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines
- Flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts
The brain is composed of a high percentage of fat, and omega-3s contribute to its structure. Incorporating foods with these fatty acids into your diet is a direct way to supply your body with them. While you manage your health, these dietary fats contribute to the building blocks available for your brain’s cells.
They are a component of a balanced diet, and their presence may support cognitive function. They may also help reduce inflammation, which is linked to various neurological conditions. Including these nutrient-rich foods in your meals regularly can be a practical step towards maintaining long-term brain health, and doing so can also support your overall well-being.
Improving Outcomes
Nutrition might also support the effectiveness of established depression treatments. When individuals receive treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), TMS therapy, or ketamine, their overall physical health may influence their response. A well-nourished body is better equipped to handle the physiological demands of treatment and recovery.
Get Treated for Depression
A combination of therapy, medical treatment, and supportive lifestyle changes may yield the most positive results for managing depression. If you are struggling with symptoms of depression, speaking with a healthcare professional is a proactive step toward feeling better. You should consult a qualified healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and explore the treatment options available to you.