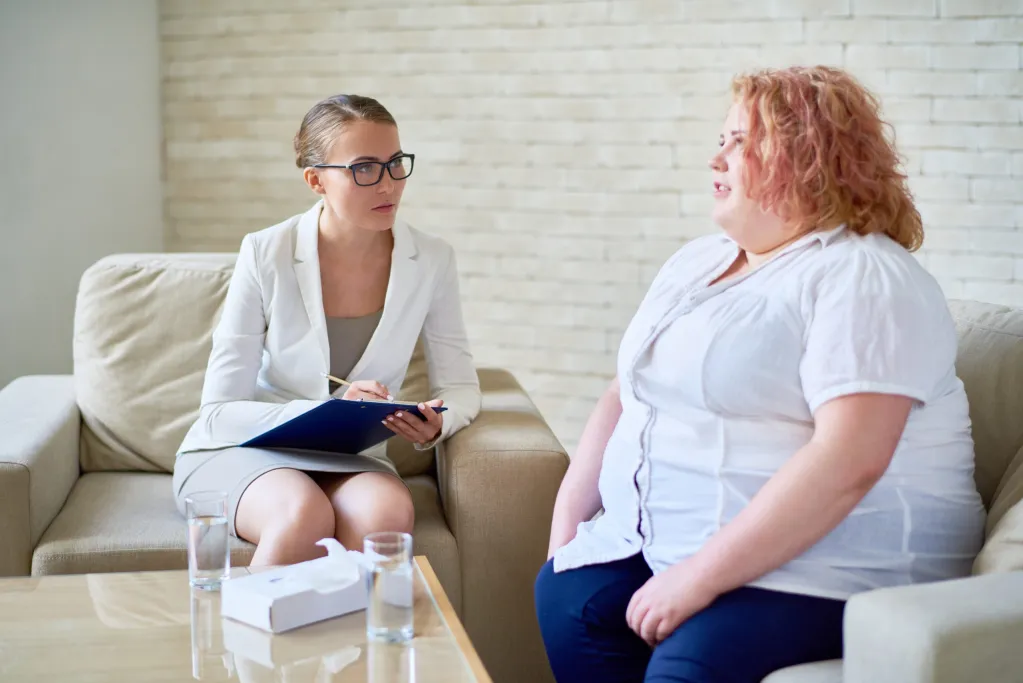
Gastric bypass surgery represents a significant step for individuals pursuing substantial weight loss and improvements in their health. The procedure alters the digestive system, which necessitates permanent adjustments to diet and lifestyle. Understanding these dietary changes is a component of a successful recovery and long-term health management.
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass is a type of bariatric surgery that modifies the stomach and small intestine. The operation changes how these organs handle the food a person consumes. The surgeon starts by creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach, effectively separating it from the larger portion of the stomach. This new, smaller stomach pouch holds significantly less food, which restricts calorie intake.
The surgeon then divides the small intestine and attaches the lower part directly to the newly created stomach pouch. This rerouting causes food to bypass most of the stomach and the first section of the small intestine. The combination of restricting food intake and reducing nutrient absorption facilitates substantial weight loss.
Who Is It For?
Medical professionals recommend gastric bypass surgery for individuals with severe obesity who have not achieved sufficient weight loss through diet and exercise alone. Candidates generally have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, which indicates severe obesity. A thorough medical evaluation is performed to assess a person’s overall health and readiness for surgery. Candidates must demonstrate a commitment to making lifelong lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications.
What Does Recovery Involve?
Recovery after gastric bypass surgery is a gradual process that involves a carefully structured diet to help the body heal and adapt. The dietary plan progresses in stages, beginning immediately after the operation. The initial stage consists of a clear liquid diet. Patients then move to a full liquid diet, which may include protein shakes, milk, and strained soups. This phase lasts for a few weeks. Following the liquid diet, the patient may transition to pureed foods. Foods can be blended to a smooth and soft consistency, which is more tolerable for the newly configured digestive system.
After a few weeks of pureed foods, the diet advances to soft foods. This stage introduces foods that are easy to chew and digest, such as cooked vegetables, soft fruits, and ground meats. About two to three months after the operation, patients can gradually reintroduce firmer foods. Long-term dietary success involves eating small, nutrient-dense meals throughout the day. Patients must focus on high-protein foods to support healing and maintain muscle mass. It may also be necessary to take prescribed vitamins and mineral supplements for life, because the procedure reduces the body’s ability to absorb certain nutrients.
Consult a Bariatric Surgeon
Gastric bypass surgery is a complex procedure that requires careful medical guidance. Anyone thinking about this type of surgery should seek a comprehensive evaluation from a qualified bariatric surgeon. A specialist can offer personalized advice, determine candidacy, and explain the benefits and risks associated with the operation. Working closely with a medical team is the best way to navigate the process safely and achieve the desired health outcomes.