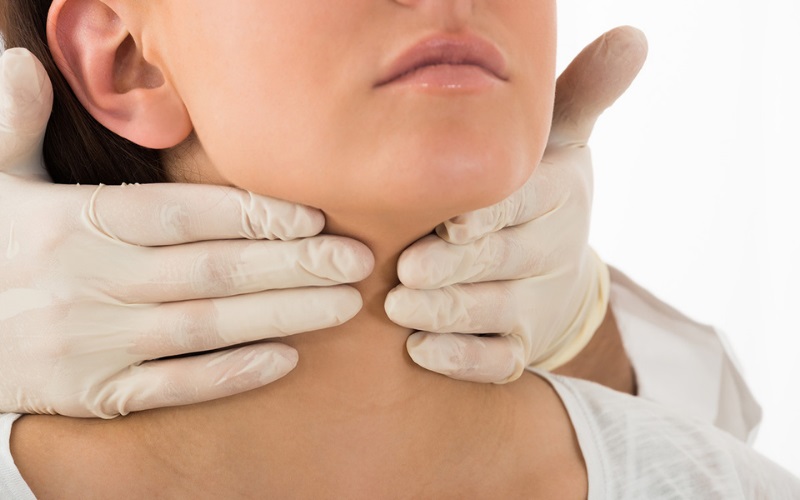
Internal medicine physicians manage a wide spectrum of adult illnesses, and they often diagnose and treat conditions affecting the endocrine system. Thyroid disease represents a hormonal imbalance that requires careful management. Because the thyroid gland regulates metabolism, an imbalance may affect multiple body systems. Here is more information about thyroid disease treatments and how they work:
1. Replacement Thyroid Hormones
For individuals with hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormone, treatment often involves synthetic thyroid hormones. A physician prescribes a specific dosage, and they will monitor the patient’s response through regular blood tests. This process restores hormone levels and manages symptoms of an underactive thyroid.
Physicians adjust the dosage over time, and this requires ongoing patient follow-up to maintain balance. The medication may substitute for a hormone that the thyroid gland is unable to produce sufficiently. Consistent, daily administration is a typical part of this treatment approach.
Finding the correct dosage is a process that requires patience, as it may take several adjustments before hormone levels stabilize. The goal is to bring the hormone level into the normal range, and patients work with their provider to track their progress. This collaboration helps in fine-tuning the treatment for the long term.
2. Thyroid Medications
When a person has hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, medication may be an option. Antithyroid drugs work by decreasing the thyroid’s ability to produce hormones. A physician determines the appropriate medication and dosage. This is typically based on the patient’s specific condition and medical history.
These medications do not offer a permanent solution for everyone, so some individuals may need additional treatments. Regular monitoring is part of the regimen, as it allows the physician to check for effectiveness and any potential side effects. The duration of the treatment varies among internal medicine clinics.
3. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine therapy is another treatment for hyperthyroidism. The patient takes a dose of radioactive iodine in liquid or capsule form, and the thyroid gland absorbs it. Since the thyroid gland actively collects iodine to make hormones, the radioactive material concentrates there and gradually destroys the gland’s cells. This procedure has specific post-treatment protocols, which may include:
- Avoiding close contact with others for a few days
- Sleeping in a separate bed
- Using separate utensils and towels
Over several weeks to months, the therapy may the thyroid’s activity and lowers hormone levels, leading to a permanent state of hypothyroidism. Healthcare providers develop treatment plans tailored to your specific diagnosis and health profile. Patients undergoing this treatment will typically require regular follow-up appointments to monitor thyroid hormone levels and ensure effective management of their condition. Long-term hormone replacement therapy with levothyroxine is often necessary to maintain normal metabolic functions after hypothyroidism develops.
Find Internal Medicine Services
Managing thyroid disease involves a partnership between you and your healthcare provider. An internal medicine physician provides the detailed oversight needed for these conditions. To learn more about how our internal medicine team can assist you, reach out to a medical professional specializing in thyroid treatment. Schedule an appointment today to discuss your health needs with a physician.